Indigo Bunting
Passerina cyanea
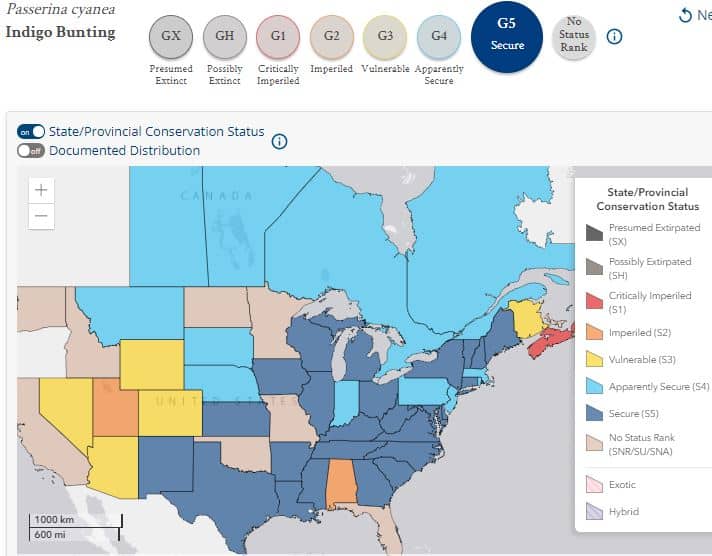
Status: Secure
The Indigo Bunting is a small, sparrow-size bird. Males, especially during mating season, are a brilliant blue while females are more of a tan color. These birds prefer to live and nest in open forest spaces, such as along the edges of a forest, or in areas that have recently burned and are just starting to grow back. These birds feed primarily on seeds, berries, and small insects.
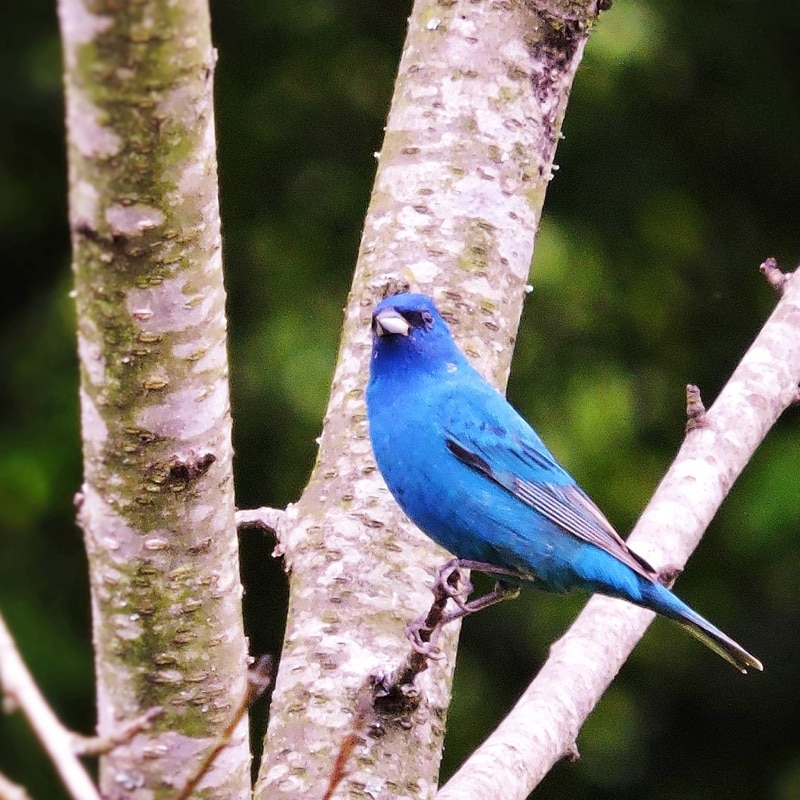
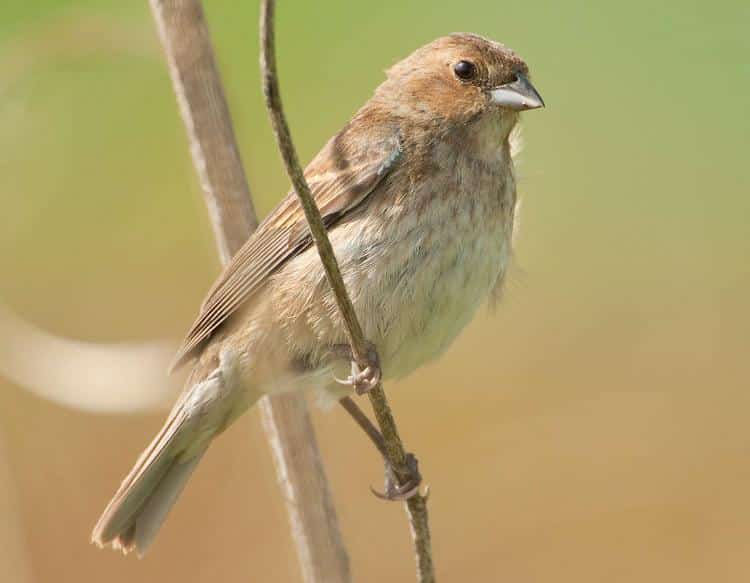


Habitat & Range
The indigo bunting can be found throughout eastern North America, and migrate to Central and South America for the winter. These birds depend on brush and grassy areas to create its nest and feed.
Food Web & Energy Flow
The indigo bunting mainly eats insects during the spring and summer months, and seeds during the winter, making it a secondary consumer. Predators, including snakes, cats, lizards, raccoons, and other types of birds, are mainly those that can climb and they mostly prey on the eggs of the indigo bunting.
Relationship to Fire
The indigo bunting is not particularly dependent on fire to maintain its habitat, as they can live in other places as well. But, for birds that have established themselves in longleaf pine forests, regular fires maintain conditions this bird does prefer.

Conservation Status
The indigo bunting is considered Secure, and is not considered at risk of going extinct.
Human Impacts/ Threats
Habitat Loss
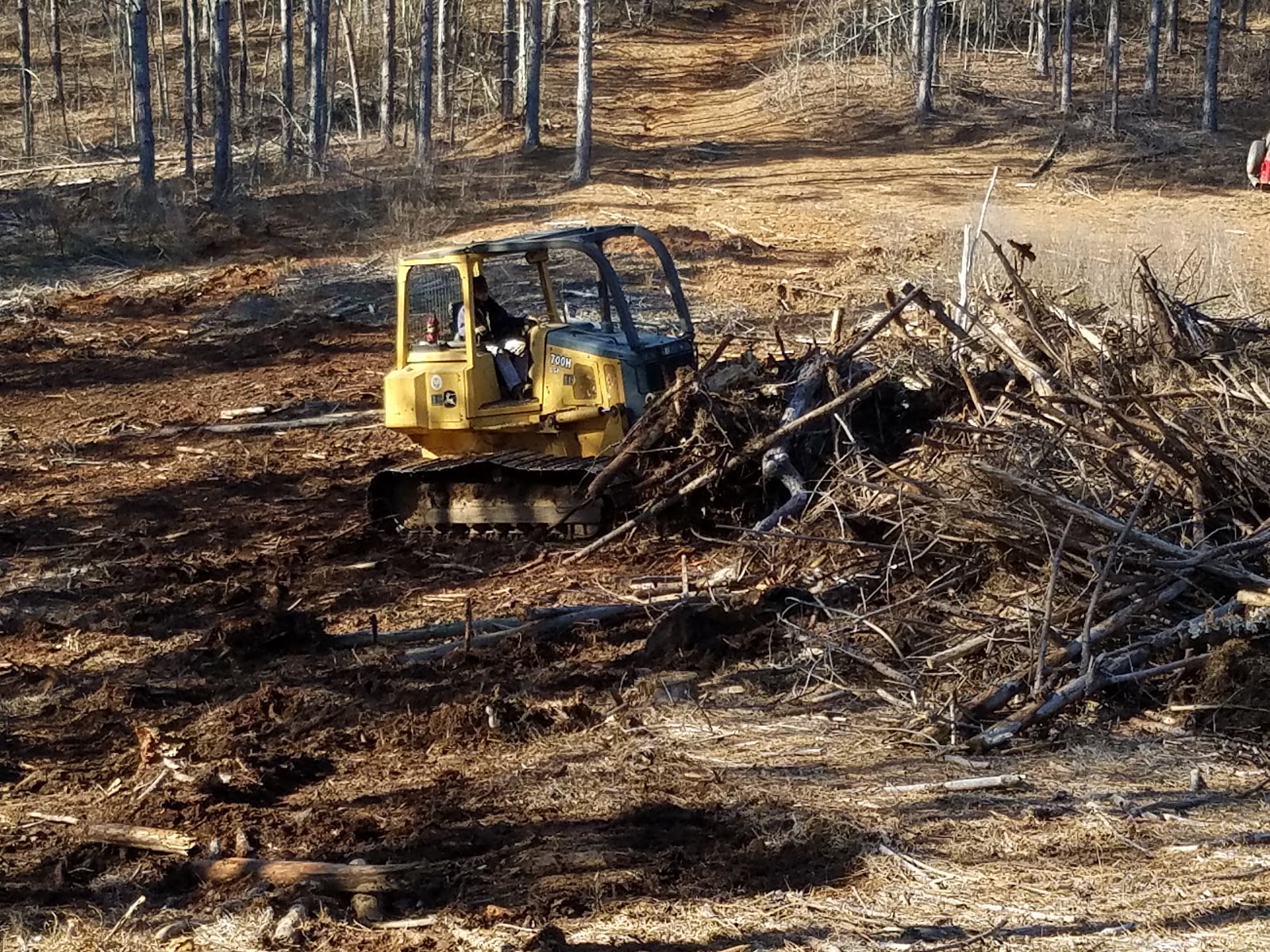

Indigo bunting needs open natural space and trees to survive. Clearing this habitat for other uses such as farming or houses is a threat to this bird species.
Animal Diversity Web. Indigo Bunting
American Bird Conservancy. Indigo Bunting
Audubon Guide to North American Birds. Indigo Bunting
