Earth
Deforestation
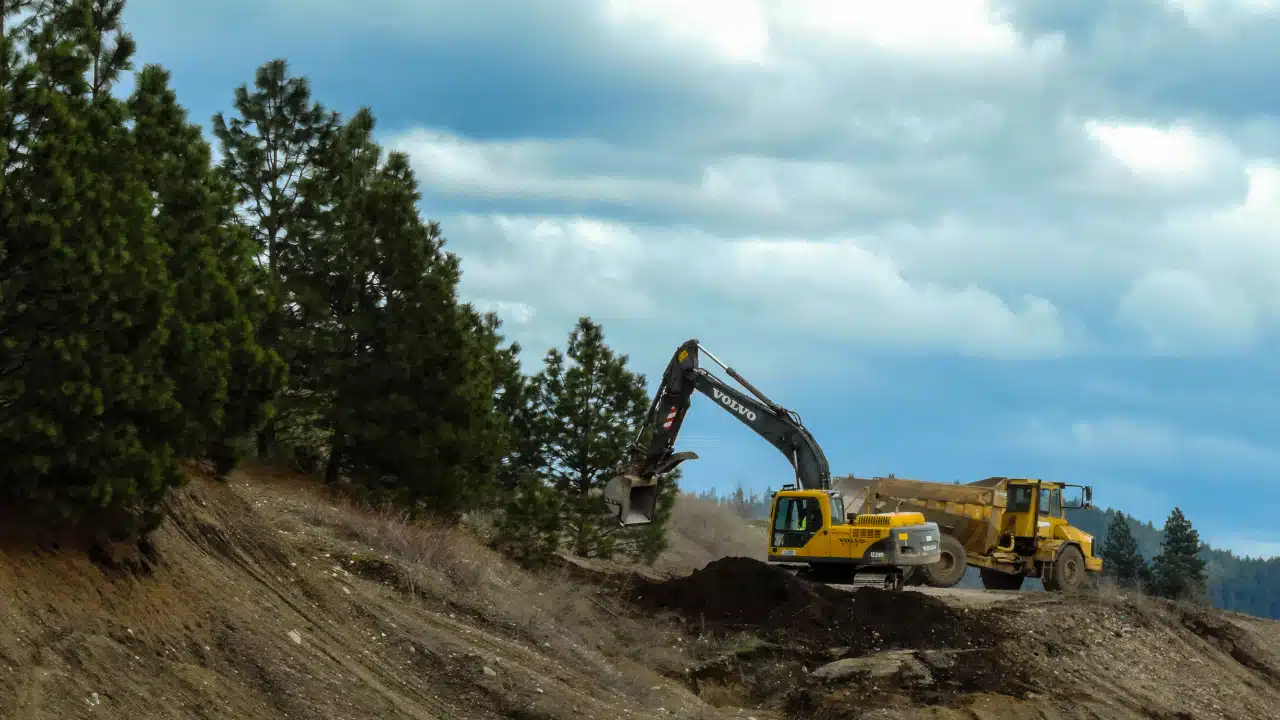

What is Deforestation?
Deforestation refers to the clearing of forested land whether it be accidental, natural, or purposefully cleared. This rampant deforestation is creating long-term problems for our environment, such as disease and desertification.
Accidental Deforestation
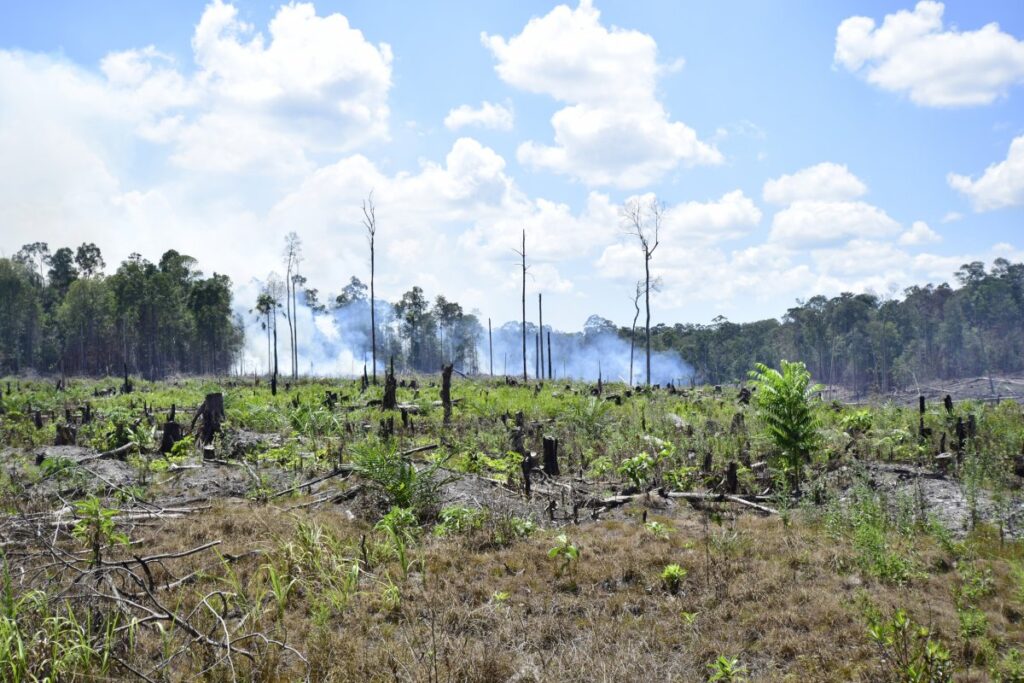

Deforestation as a result of forest fires or unexpected effects of logging.
Natural Deforestation
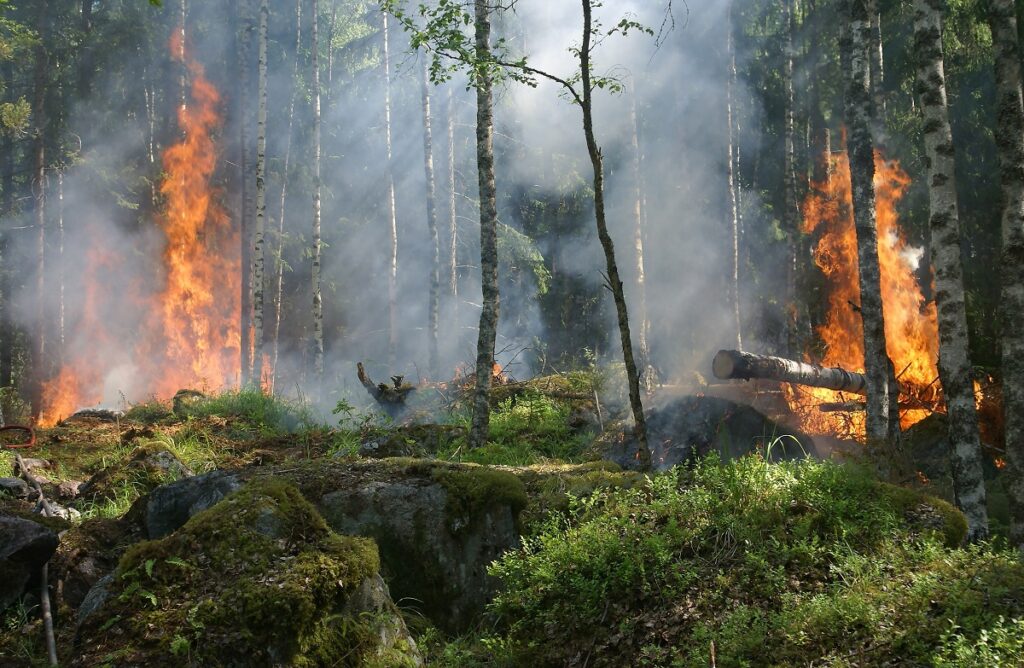

Deforestation as a result of natural disasters such as floods or tornados.
Purposeful Deforestation
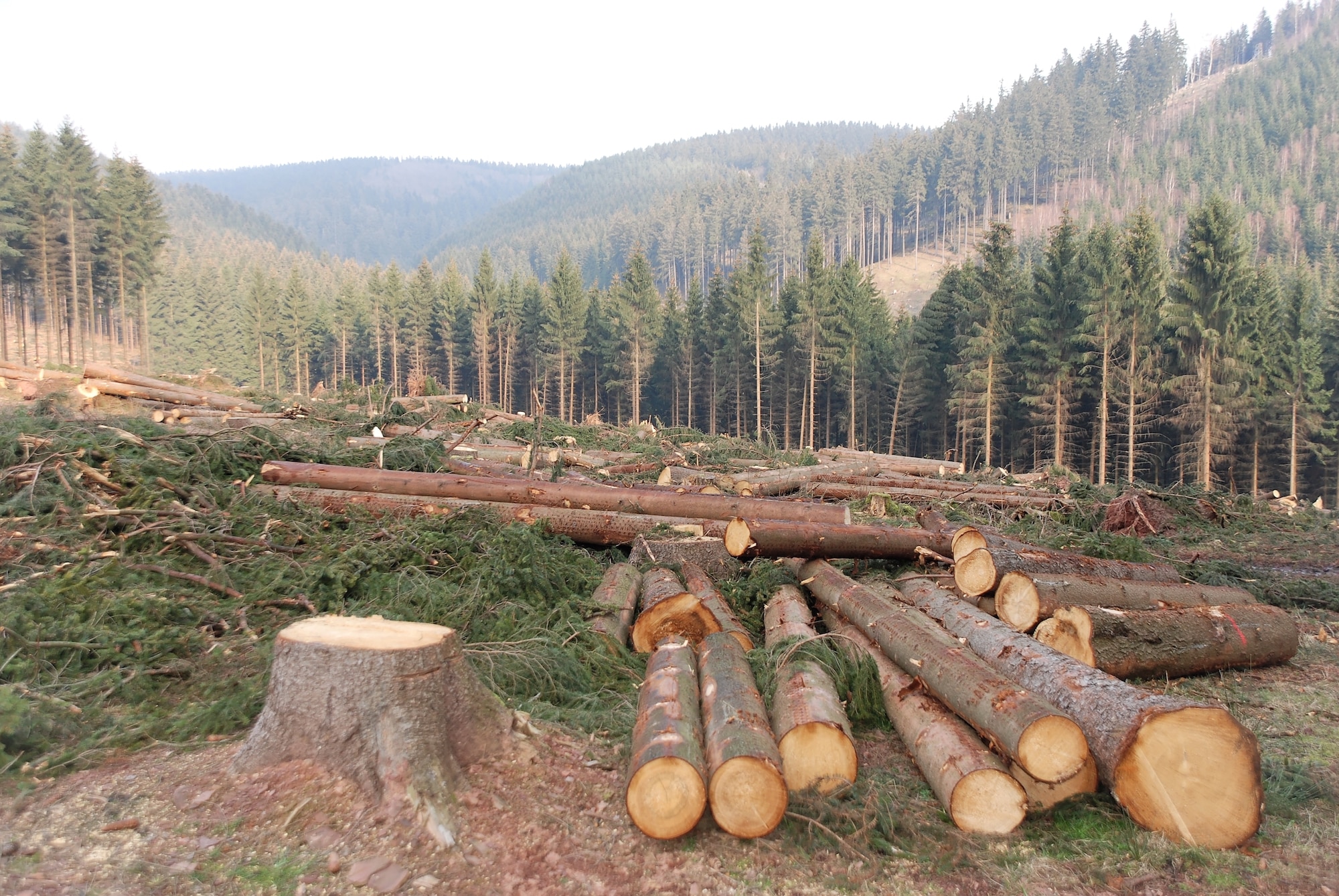

Deforestation caused by humans cutting trees for material use.
This rampant deforestation is creating long-term problems for our environment, such as disease and desertification.
Desertification
Deforestation disrupts ecosystems and can transform fertile lands into deserts. This transformation is known as desertification.
Desertification leads to what is known as a “positive feedback loop”. A positive feedback loop is when one change in an environment leads to a secondary change. This secondary change in turn makes the first one even worse.
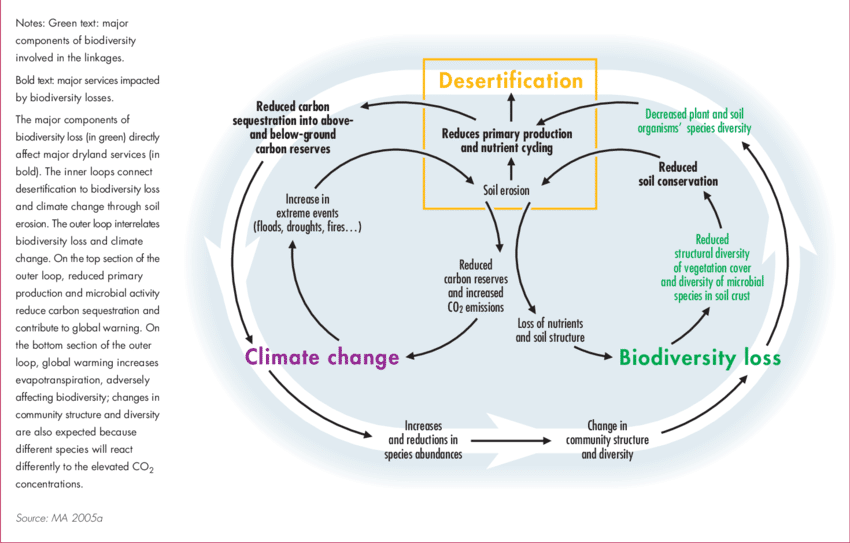
When looking at desertification, we first see a change in the environment from deforestation. Deforestation then leads to the second change: loose and dry topsoil. Without root anchors and incoming water, soil becomes brittle and inhabitable. This feedback loop continues, leading to poor soil quality and making it harder and harder for plants to grow.
While this issue is primarily seen in the global southern and eastern regions, it is becoming a larger concern for the United States, with 17 states (mostly those in the west) under threat of this process.
Infectious Disease
Around 80% of the earth’s plants and animals call forests home including deer, birds, bats and more. When forests are cleared, these animals lose their homes and become displaced. As land is cleared and more animals become displaced, they are more likely to come in contact with humans. This leads to an an increased risk of zoonotic diseases.
Zoonotic diseases are the term for disease passed to humans from animals. Nearly half of the world’s infectious diseases are zoonotic, with well known ones including Lyme disease, Malaria, and COVID-19.
Below shows a chart of Lyme Disease cases in North America:
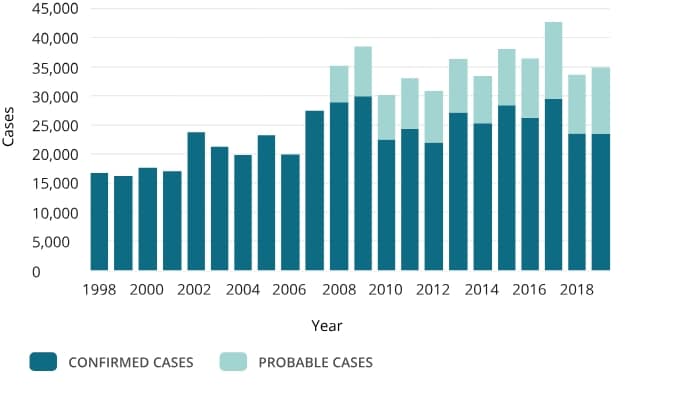
Dilution effect is the understanding that wide biodiversity causes less spread of disease, as not all species can be affected by varying types of illness. As animals' homes are destroyed, some species will leave a location altogether causing a decrease in biodiversity. If species diminish, the chance that those still in an area will be able to carry a disease grows.
What is the importance of soil?

